Fraud is a deliberate act of deception designed to secure an unfair or unlawful gain. In today’s interconnected world, fraudulent schemes have become more sophisticated, making it essential for individuals and businesses to recognize warning signs and take proactive measures.
Understanding the different types of fraud and how they operate is the first step toward protecting yourself, your assets, and your reputation.
Common Types of Fraud
Fraud comes in many forms, affecting individuals, corporations, and even entire industries. Below are some of the most prevalent types, along with how they work.
1. Identity Theft
Identity theft occurs when someone uses your personal information, such as your name, Social Security number, or bank details, without your permission. Criminals may open new credit accounts, make unauthorized purchases, or even commit crimes in your identity. Victims often face a long recovery process involving financial losses, credit score damage, and emotional stress. In severe cases, it can take years to fully clear your records. The impact is not just monetary; it can disrupt your daily life.
Prevention Tips:
- Shred any documents containing personal information before disposing of them.
- Use strong, unique passwords for all accounts, and change them regularly.
- Avoid sharing personal details on social media.
- Review your bank and credit card statements frequently.
- Set up credit monitoring services to detect suspicious activity early.
2. Investment Fraud
Investment fraud involves misleading or deceiving people into placing money into false or risky ventures. Scammers may promise high returns with little to no risk, which is often unrealistic. Common schemes include Ponzi schemes, fake stock tips, and unregistered securities. These scams often target retirees or those seeking quick financial growth. Once the fraud is discovered, recovering the money is usually very difficult.
Prevention Tips:
- Be skeptical of investments promising guaranteed returns.
- Research the company and check its registration with regulatory bodies.
- Avoid rushing into financial decisions under pressure.
- Consult a licensed financial advisor before investing.
- Keep detailed records of all investment agreements.
3. Insurance Fraud
Insurance fraud happens when someone intentionally deceives an insurance provider for personal gain. This could involve exaggerating claims, staging accidents, or providing false information during policy applications. Fraudulent claims increase overall costs for all policyholders through higher premiums. Insurers also spend significant resources investigating and combating these activities.
Prevention Tips:
- Provide accurate information when applying for insurance coverage.
- Keep all receipts, photos, and evidence when filing legitimate claims.
- Report suspicious claims or staged incidents to your insurer.
- Avoid working with repair shops or third parties that suggest falsifying claims.
- Review your policy terms so you understand what is covered.
4. Healthcare Fraud
Healthcare fraud includes billing for services not provided, overcharging, or using false diagnoses to claim insurance payments. It can be committed by healthcare providers, patients, or third parties. This type of fraud not only causes financial loss but also undermines trust in the healthcare system. It can also put patients at risk when unnecessary treatments are administered.
Prevention Tips:
- Check your medical bills for services you didn’t receive.
- Keep personal insurance information secure.
- Use healthcare providers with good reputations and proper licenses.
- Report suspicious billing to your insurance company immediately.
- Ask for an itemized bill for all treatments.
5. Payment Fraud
Payment fraud happens when unauthorized transactions are made using your payment details. This includes credit card fraud, debit card fraud, and bank account breaches. It can occur through physical theft or online hacking. Victims may notice unauthorized withdrawals, unexpected charges, or duplicate transactions. Quick action is crucial to minimize losses.
Prevention Tips:
- Monitor your bank statements and online accounts regularly.
- Avoid entering payment details on unsecured websites.
- Use two-factor authentication where available.
- Never share your PIN or banking password.
- Report lost or stolen cards immediately to your bank.
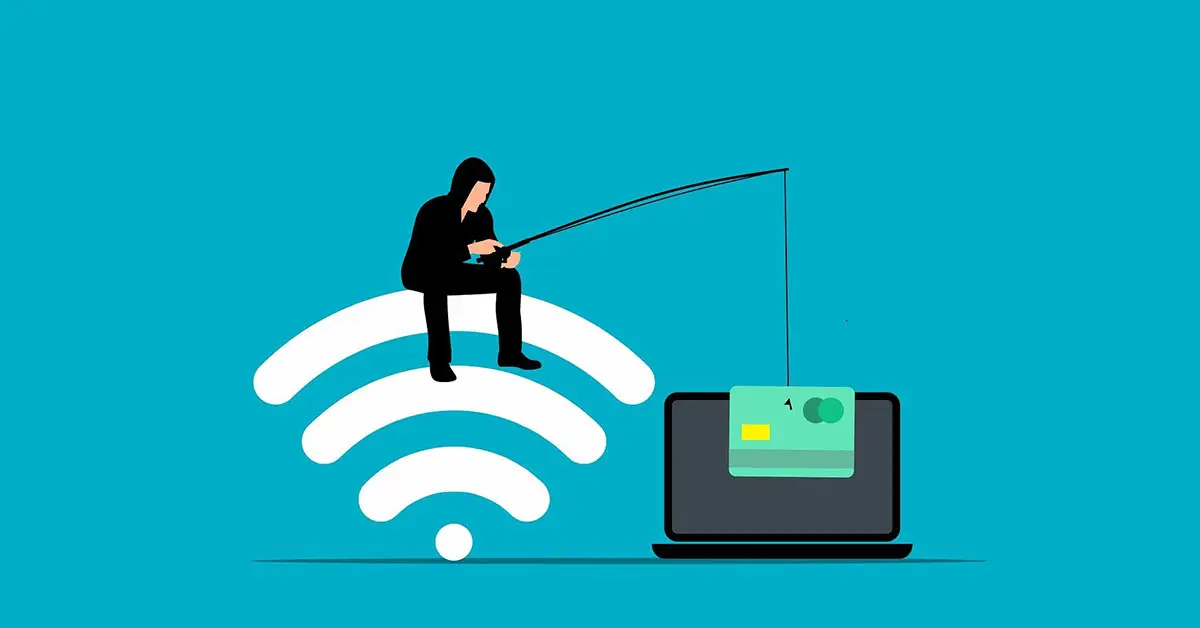
6. Online Scams
Online scams range from phishing emails to fake online stores and romance scams. Scammers use email, social media, or fake websites to trick victims into sending money or revealing sensitive information. These scams often play on emotions, such as fear or love, to manipulate victims. They are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making them harder to detect.
Prevention Tips:
- Do not click on suspicious links or attachments.
- Check website addresses for small spelling errors that indicate fake sites.
- Be cautious when forming online relationships with strangers.
- Verify online sellers through reviews and ratings.
- Use secure payment methods for online purchases.
7. Corporate Fraud
Corporate fraud involves illegal activities carried out within a company for personal or organizational gain. Examples include falsifying financial records, insider trading, and hiding liabilities. This type of fraud can damage shareholder trust, lead to job losses, and cause severe financial losses. It often requires thorough investigations to uncover.
Prevention Tips:
- Companies should implement strong internal controls.
- Employees should report suspicious activity anonymously through whistleblower programs.
- Regular audits can help detect irregularities.
- Maintain transparency in all financial reporting.
- Provide fraud-awareness training for employees.
8. Loan Fraud
Loan fraud occurs when false information is provided to secure a loan. This could be for personal loans, mortgages, or business funding. Fraudsters might fake income statements, alter credit reports, or hide debts. Such actions can result in loan defaults and financial instability for lenders.
Prevention Tips:
- Lenders should verify all borrower information through reliable sources.
- Borrowers must be truthful in all applications.
- Use secure channels when submitting financial documents.
- Keep copies of all submitted loan applications.
- Report suspicious loan offers that seem too good to be true.
9. Bankruptcy Fraud
Bankruptcy fraud happens when individuals or businesses hide assets or falsify information during bankruptcy proceedings. The aim is often to avoid paying creditors or to protect assets illegally. This undermines the fairness of the process and can lead to serious penalties.
Prevention Tips:
- Be honest when declaring all assets and debts.
- Work with a licensed bankruptcy attorney.
- Keep detailed records of all financial transactions.
- Avoid transferring property or money before filing.
- Report any suspected fraud to the relevant authorities.
10. Tax Fraud
Tax fraud involves deliberately falsifying information on tax returns to reduce tax liability. This can include underreporting income, inflating deductions, or hiding money in offshore accounts. Tax fraud reduces government revenue and can lead to heavy penalties.
Prevention Tips:
- File accurate and complete tax returns.
- Keep all income and expense records organized.
- Use reputable tax preparation services.
- Report all sources of income, even from side jobs.
- Avoid tax schemes promoted by unverified sources.
11. Vendor Fraud
Vendor fraud occurs when a supplier overcharges or delivers substandard products while charging full price. This can happen in both private businesses and government contracts. It can lead to financial loss and damage business relationships.
Prevention Tips:
- Compare prices and services with multiple suppliers.
- Check the quality of goods upon delivery.
- Maintain detailed contracts outlining product standards.
- Conduct periodic supplier audits.
- Avoid long-term agreements without regular performance reviews.
12. Charity Fraud
Charity fraud happens when individuals or groups solicit donations for fake causes. Victims believe they are supporting a good cause, but their money is misused. These scams often appear after natural disasters or during holiday seasons.
Prevention Tips:
- Research the charity before donating.
- Verify that it is registered with the proper authorities.
- Avoid giving money in cash; use traceable payment methods.
- Be cautious of high-pressure donation tactics.
- Ask for receipts for all donations.
13. Counterfeiting
Counterfeiting involves producing fake currency, documents, or goods with the intent to deceive. This includes fake passports, fake designer goods, and forged checks. It harms legitimate businesses and can cause legal trouble for those caught with counterfeit items.
Prevention Tips:
- Learn how to identify authentic security features in currency.
- Purchase goods only from trusted retailers.
- Use secure payment methods for large transactions.
- Check product authenticity codes where available.
- Report suspected counterfeit goods to authorities.
Civil Fraud vs Criminal Fraud
Fraud can fall into two legal categories: civil or criminal, depending on the severity and intent.
Civil Fraud
Civil fraud involves deception that causes financial or property damage but does not necessarily rise to the level of a criminal offense. The outcome typically involves monetary compensation to the victim.
Example:
A business misrepresents a product’s quality, leading to financial loss for the buyer.
Consequences:
- Monetary damages
- Court orders to correct the wrongdoing
- No imprisonment
Criminal Fraud
Criminal fraud involves intentional deception that violates criminal laws. This can include theft, forgery, or embezzlement. Prosecutors must prove intent beyond a reasonable doubt.
Example:
A person forges checks to withdraw money from another person’s bank account.
Consequences:
- Fines
- Imprisonment
- Criminal record
Practical Steps to Avoid Fraud
Avoiding fraud requires both awareness and action. Here are some practical strategies:
- Educate Yourself Continuously: Stay updated on the latest scams through news outlets and official advisories.
- Verify Before Trusting: Always confirm the legitimacy of individuals, businesses, and organizations before sharing information or money.
- Protect Personal Data: Use encryption tools, shred sensitive documents, and avoid oversharing online.
- Use Secure Technology: Enable two-factor authentication, keep software updated, and use reputable antivirus programs.
- Report Suspicious Activity: Alert authorities, your bank, or consumer protection agencies at the first sign of fraud.
Final Thoughts
Fraud is a global issue that affects millions each year, costing individuals and organizations billions of dollars. By understanding the most common types of fraud and the differences between civil and criminal cases, you can better safeguard yourself against potential threats. Awareness is your first line of defense, but proactive habits like verifying sources, securing your data, and knowing your legal rights are equally important. The more you know, the harder it is for fraudsters to succeed.
Sources
1. https://www.cgteam.com 2. Stripe https://stripe.com Six types of payment fraud—and how businesses can prevent them 3.https://www.tookitaki.com/



















Add comment