Professional OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology for financial document extraction is used to convert bank statements, invoices, receipts, tax forms, and other financial records into structured, machine-readable data with high accuracy. It combines image processing, AI-based text recognition, layout analysis, and data validation to extract key fields like transaction dates, amounts, account numbers, and vendor names. When implemented correctly, it reduces manual data entry by up to 80–90%, improves compliance, and speeds up reconciliation and reporting.
This tutorial explains how professional OCR works in financial workflows, how to implement it step by step, and what to look for when choosing the right solution.
What Is OCR and Why It Matters in Finance?
OCR is the process of converting images of text such as scanned PDFs, photos, or faxes into editable and searchable digital text. In financial environments, OCR goes far beyond simple text reading. It must understand structured and semi-structured documents, identify tables, and correctly extract critical numerical data.
Financial documents are dense, repetitive, and sensitive. A small mistake in reading a decimal or negative value can lead to reporting errors. That’s why professional OCR for finance is different from generic OCR used for books or articles. It needs:
- Field-level extraction (date, description, debit, credit, balance)
- Table detection and parsing
- High numerical accuracy
- Multi-format handling (PDF, JPEG, TIFF)
- Validation rules for financial logic
Without OCR, companies rely on manual data entry. That’s slow, costly, and error-prone.
Types of Financial Documents OCR Can Extract
Professional OCR systems are trained specifically on financial formats. Each document type requires different parsing logic.
Bank Statements
Bank statements contain structured transaction tables. A robust OCR engine must detect:
- Statement period
- Account number
- Opening and closing balances
- Transaction rows (date, description, debit, credit, balance)
Table recognition is critical here. The system must keep row alignment intact.
Invoices
Invoices are semi-structured. Layout varies widely between vendors. OCR must identify:
- Vendor name
- Invoice number
- Invoice date
- Line items
- Tax
- Total amount
Unlike bank statements, invoice layouts differ significantly across businesses. AI-based layout learning becomes essential.
Receipts
Receipts are often photographed rather than scanned. They may be skewed, blurred, or faded. OCR for receipts must include:
- Image enhancement
- Skew correction
- Text cleaning
- Vendor recognition
Tax Forms and Financial Reports
Tax forms and financial reports require structured field extraction and compliance validation. Errors here can create regulatory issues.
How Professional OCR Technology Works (Step-by-Step)
Professional OCR for financial document extraction follows a structured pipeline. Understanding this workflow helps you implement it properly.
1. Image Preprocessing
Before text recognition, documents are cleaned:
- Noise removal
- Skew correction
- Contrast enhancement
- Resolution normalization
Preprocessing directly affects accuracy. Low-quality scans reduce recognition performance.
2. Text Recognition Engine
Modern systems use deep learning models rather than traditional rule-based OCR. These models:
- Recognize printed fonts
- Handle multiple languages
- Interpret distorted characters
- Detect numeric precision
Financial OCR focuses heavily on numeric recognition accuracy.
3. Layout and Table Detection
This is where professional solutions differ from basic OCR.
Instead of extracting plain text, advanced systems:
- Identify columns
- Detect table rows
- Map cell relationships
- Preserve financial structure
Without table parsing, transaction data becomes unusable.
4. Field Mapping and Data Extraction
The system maps extracted text into structured fields:
- Transaction date
- Amount
- Currency
- Vendor
- Account number
This step converts raw text into usable financial data formats like CSV, JSON, or XML.
5. Validation and Error Detection
Financial OCR includes validation logic such as:
- Debit + Credit reconciliation
- Running balance checks
- Date consistency validation
- Duplicate detection
This dramatically reduces financial reporting risks.
Manual Entry vs Professional OCR: Cost and Accuracy Comparison
Implementing OCR often comes down to cost and efficiency. Here’s a practical comparison:
| Factor | Manual Data Entry | Professional OCR |
| Processing speed | Slow | Fast |
| Human error rate | 1–3% typical | <0.5% with validation |
| Labor cost | High ongoing | Lower long-term |
| Scalability | Limited | Easily scalable |
| Audit trail | Manual logs | Automated tracking |
For high-volume financial operations, OCR typically pays for itself quickly.
Implementation Guide: How to Deploy OCR for Financial Extraction
Here’s a practical implementation roadmap.
Step 1: Define Document Scope
Identify:
- Document types (bank statements, invoices, etc.)
- Expected monthly volume
- Required output format
- Integration endpoints (ERP, accounting software)
Clear scope reduces implementation delays.
Step 2: Choose the Right OCR Technology
Look for:
- Financial document specialization
- High numeric accuracy
- Table detection capabilities
- API integration support
- Data security compliance
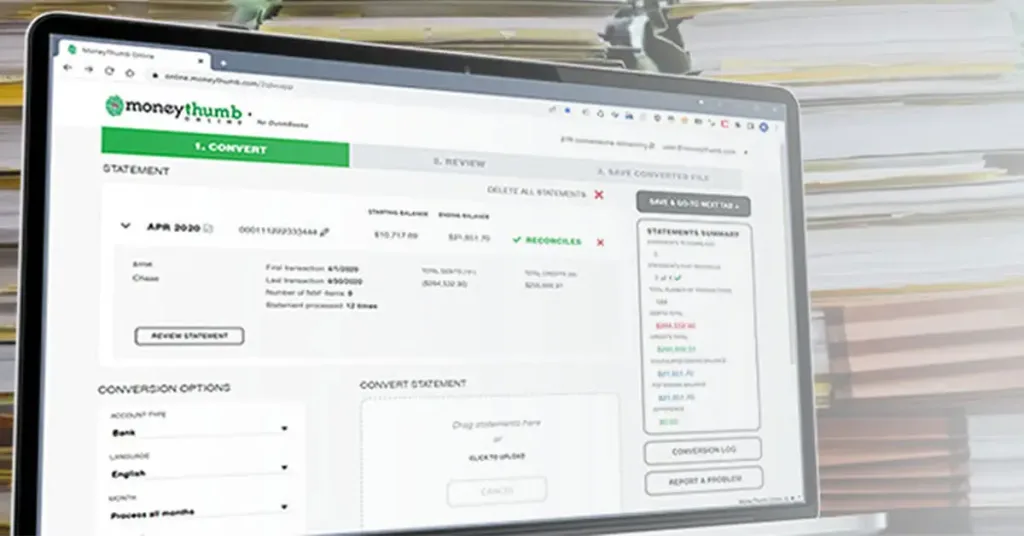
Some providers offer specialized financial extraction tools. For example, solutions like moneythumb's OCR focus specifically on extracting structured financial data from bank statements and similar documents, making them suitable for accounting workflows without requiring custom development.
Step 3: Integrate with Accounting Systems
OCR output should feed directly into:
- QuickBooks
- Xero
- ERP systems
- Data warehouses
API-based integration prevents manual uploads.
Step 4: Test Accuracy with Real Documents
Run test batches including:
- Clean scans
- Low-quality scans
- Different bank formats
- Multi-page statements
Measure extraction accuracy before full deployment.
Step 5: Implement Validation Rules
Define:
- Balance checks
- Currency normalization
- Date formatting rules
- Negative value handling
Validation protects financial integrity.
Common Challenges in Financial OCR (and How to Solve Them)
Even professional OCR systems face challenges. Here’s how to address them.
1. Poor Image Quality
Solution:
- Require minimum DPI standards
- Use automated image enhancement
- Encourage digital PDFs instead of photos
2. Complex Table Layouts
Solution:
- Use AI-based table detection
- Train models on sample layouts
- Use template mapping when consistent
3. Multiple Bank Formats
Solution:
- Deploy layout-learning OCR
- Use template libraries
- Continuously update model training
4. Handwritten Notes
Handwriting is harder than printed text.
Solution:
- Use advanced handwriting recognition models
- Flag uncertain characters for review
Security and Compliance in Financial OCR
Financial documents contain sensitive information. OCR systems must comply with:
- Data encryption in transit and at rest
- Access controls
- Role-based permissions
- Audit logs
- Secure API endpoints
When selecting a provider, verify compliance standards and data handling policies.
Never upload financial documents to unsecured platforms.
Performance Metrics You Should Track
To evaluate your OCR system, monitor:
- Field-level accuracy rate
- Table extraction accuracy
- Processing time per document
- Exception rate
- Manual correction frequency
These metrics determine ROI and operational improvement.
AI and Machine Learning in Modern OCR
Traditional OCR relied heavily on character matching. Modern financial OCR uses:
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)
- Transformer-based models
- Context-aware number recognition
- Layout analysis models
These technologies improve recognition even in non-standard layouts.
Machine learning models also improve over time with more document samples.
Best Practices for High-Accuracy Financial Extraction
To maximize OCR performance, follow these principles:
After testing multiple implementations, certain patterns consistently improve results:
- Use consistent document formats where possible
- Standardize scanning resolution (300 DPI minimum recommended)
- Automate validation rules
- Monitor exception logs weekly
- Retrain models periodically
Consistency reduces downstream errors.
When Should You Use Professional OCR?
OCR becomes essential when:
- Processing more than 100 financial documents monthly
- Managing multi-bank reconciliation
- Scaling accounting teams
- Automating loan underwriting
- Handling audit-heavy environments
If data entry consumes significant staff time, OCR is no longer optional.
Real-World Use Cases
Accounting Firms
Automate client bank statement imports.
Fintech Companies
Extract transaction history for risk analysis.
Loan Underwriting
Analyze borrower financial statements quickly.
Corporate Finance Teams
Reconcile accounts at scale.
Professional OCR turns unstructured financial documents into structured financial intelligence.
FAQs
What accuracy can professional OCR achieve for financial documents?
Most professional systems achieve 95–99% field-level accuracy depending on document quality and layout complexity.
Can OCR extract tables from bank statements accurately?
Yes, advanced financial OCR systems include table detection and structured row mapping, which preserve transaction alignment.
Is OCR secure for handling bank statements?
It can be secure if the provider uses encryption, strict access controls, and compliance-grade data protection standards.
Does OCR work with scanned PDFs and photos?
Yes. Professional systems support scanned PDFs, images (JPEG, TIFF), and even mobile-captured receipts.
Conclusion
Professional OCR (Optical Character Recognition) technology for financial document extraction enables organizations to convert complex financial documents into structured, accurate, and usable data. It reduces manual effort, lowers error rates, and improves reporting efficiency. By combining image preprocessing, AI-based recognition, table detection, and financial validation rules, modern OCR systems can handle bank statements, invoices, receipts, and tax forms at scale.
When implemented properly with validation, integration, and security controls OCR becomes a foundational part of financial automation.
References
- https://www.ibm.com/topics/optical-character-recognition
- https://cloud.google.com/vision/docs/ocr
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/computer-vision/overview-ocr
- https://aws.amazon.com/textract/
- https://www.adobe.com/acrobat/resources/ocr.html
- https://www.moneythumb.com
- https://www.tesseract-ocr.github.io/
- https://www.mckinsey.com/capabilities/operations/our-insights/the-automation-advantage
- https://www2.deloitte.com/us/en/pages/finance/articles/finance-automation.html
- https://www.gartner.com/en/information-technology/glossary/optical-character-recognition-ocr











Add comment